| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- applicationeventpublisher
- Greedy
- 최단경로
- 문자열
- 파이썬
- brute force
- error
- counting elements
- 탐욕법
- spring security
- BFS
- java
- 프로그래머스
- 알고리즘
- 소수
- 2981
- springboot
- codility
- API
- javascript
- 백준
- 2018 KAKAO BLIND RECRUITMENT
- beandefinitionstoreexception
- Python
- 라이브템플릿
- 코딩테스트
- Spring
- Dijkstra
- algorithm
- HTTP
Archives
- Today
- Total
Altiora Petamus
DFS와 BFS 본문
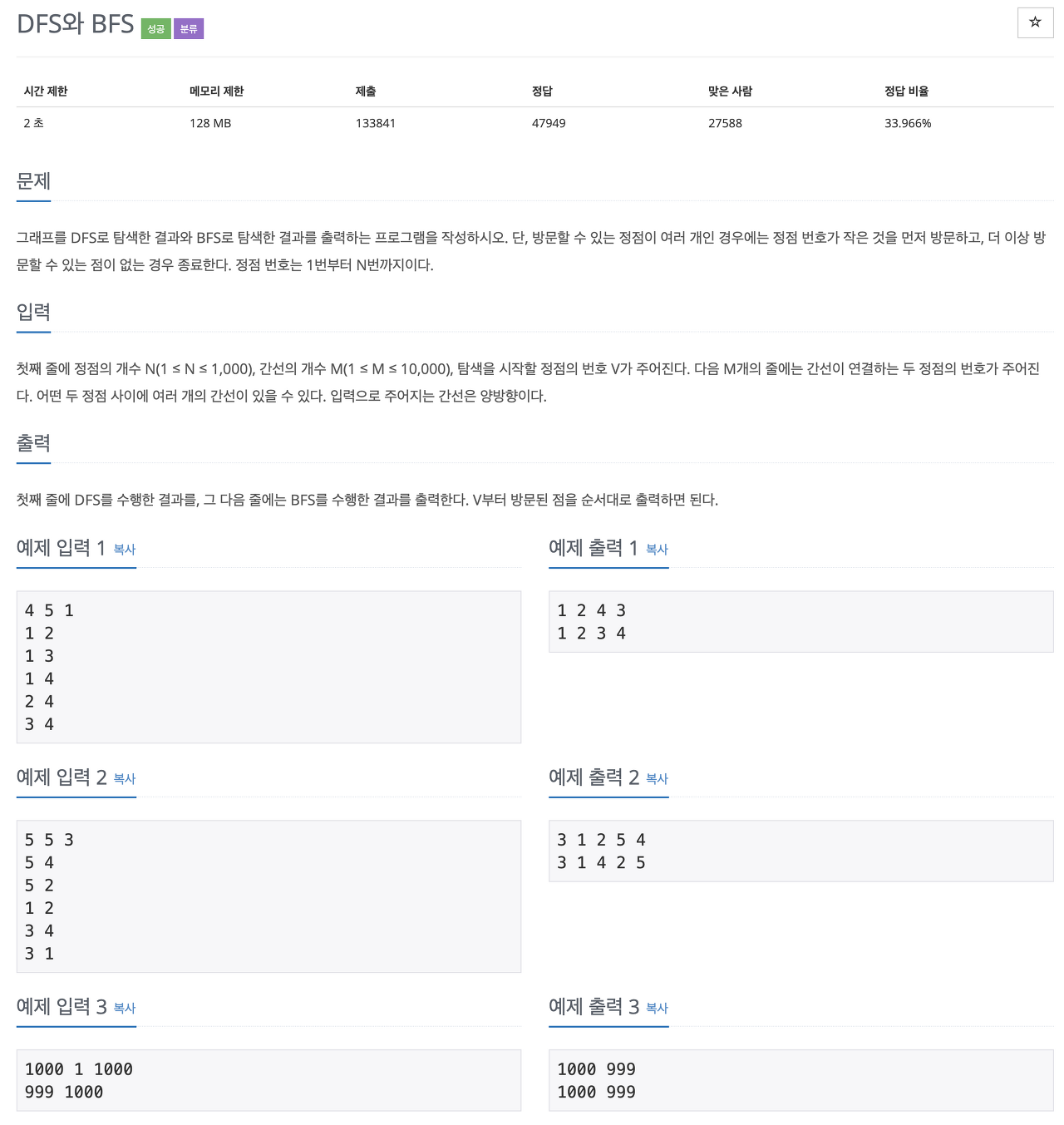
1260번: DFS와 BFS
첫째 줄에 정점의 개수 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000), 간선의 개수 M(1 ≤ M ≤ 10,000), 탐색을 시작할 정점의 번호 V가 주어진다. 다음 M개의 줄에는 간선이 연결하는 두 정점의 번호가 주어진다. 어떤 두 정점 사
www.acmicpc.net
🤔생각해보기
DFS와 BFS의 기본 개념을 익히기 위한 문제다.
자바에서는 2차원 배열로 edge 들을 설정한 뒤에 해결했었는데 파이썬에서 딕셔너리를 활용하여 풀어보았다. 개인적으로는 2차원 배열이 가독성이 끔찍하다고 느껴져서인지 어려워하는 편인데 딕셔너리를 활용해보니 이해하기도 편하고 훨씬 쉽게 해결 할 수 있는 것 같다.
성공 코드
from collections import deque
from collections import defaultdict
# stack 으로 구현
def dfs(g, r):
stack = [r]
visited = []
while stack:
n = stack.pop()
if n not in visited:
visited.append(n)
temp = list(set(g[n]) - set(visited))
# 작은 것부터 방문하기 위해 뒤에서부터 꺼내는 스택의 특성을 고려하여 내림차순으로 정렬 후 기존 스택에 추가.
temp.sort(reverse=True)
stack += temp
return visited
# deque 로 구현
def bfs(g, r):
queue = deque([r])
visited = []
while queue:
n = queue.popleft()
if n not in visited:
visited.append(n)
temp = list(set(g[n]) - set(visited))
# 앞에서부터 꺼내는 특성을 고려하여 오름차순으로 정렬 후 기존 deque 에 추가.
temp.sort()
queue += temp
return visited
N, M, V = map(int, input().split())
graph = defaultdict(list)
for _ in range(M):
n1, n2 = map(int, input().split())
# 양방향 그래프
if n1 not in graph:
graph[n1] = [n2]
elif n2 not in graph[n1]:
graph[n1].append(n2)
if n2 not in graph:
graph[n2] = [n1]
elif n1 not in graph[n2]:
graph[n2].append(n1)
print(*dfs(graph, V))
print(*bfs(graph, V))defaultdict(list): 딕셔너리에 없는 키를 호출할 때 생기는 KeyError 를 해결하기 위해 사용
'1day-1algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 수 찾기 (0) | 2021.06.15 |
|---|---|
| 베르트랑 공준 (0) | 2021.06.12 |
| binary gap (0) | 2021.06.10 |
| 소수 (0) | 2021.06.07 |
| 소인수분해 (0) | 2021.05.29 |



